Note
Click here to download the full example code
Inspect or rehearse a plan (“simulation mode”)¶
Problem¶
Check a plan for mistakes before running it on real hardware.
Approach¶
Display the steps of a plan and read through them to verify that they match our intention.
Execute the plan on “simulated hardware,” Python objects that stand in for real motors and detectors but do not actually communicate with any hardware.
Example Solutions¶
The bluesky.examples module includes simulated motors and detectors.
# Make a RunEngine instance.
from bluesky import RunEngine
RE = RunEngine({})
from ophyd.sim import motor, motor1, motor2, det
from bluesky.simulators import print_summary, plot_raster_path
from bluesky.plans import count, scan, outer_product_scan
Inspect plans¶
Use print_summary which translates the plan into a human-readable list
of steps.
print_summary(count([det]))
print_summary(scan([det], motor, 1, 3, 3))
print_summary(outer_product_scan([det], motor1, 1, 3, 3, motor2, 1, 2, 2, False))
Out:
=================================== Open Run ===================================
Read ['det']
================================== Close Run ===================================
=================================== Open Run ===================================
motor -> 1.0
Read ['det', 'motor']
motor -> 2.0
Read ['det', 'motor']
motor -> 3.0
Read ['det', 'motor']
================================== Close Run ===================================
=================================== Open Run ===================================
motor1 -> 1.0
motor2 -> 1.0
Read ['det', 'motor1', 'motor2']
motor2 -> 2.0
Read ['det', 'motor1', 'motor2']
motor1 -> 2.0
motor2 -> 1.0
Read ['det', 'motor1', 'motor2']
motor2 -> 2.0
Read ['det', 'motor1', 'motor2']
motor1 -> 3.0
motor2 -> 1.0
Read ['det', 'motor1', 'motor2']
motor2 -> 2.0
Read ['det', 'motor1', 'motor2']
================================== Close Run ===================================
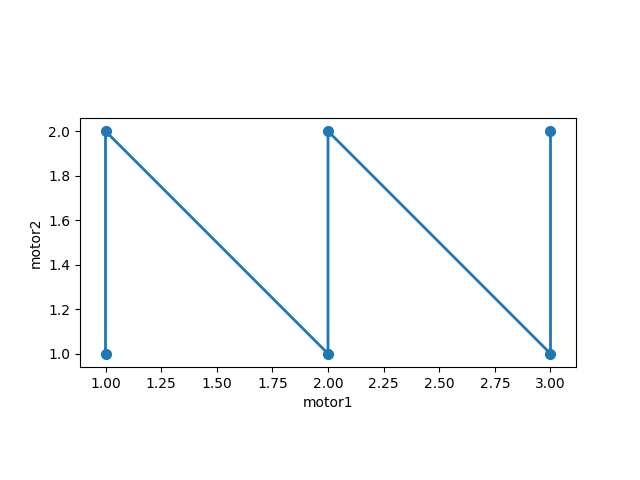
Use plot_raster_path to visualize a two-dimensional trajectory.
plot_raster_path(outer_product_scan([det], motor1, 1, 3, 3, motor2, 1, 2, 2, False),
'motor1', 'motor2')
Note that print_summary cannot be used on plans the require feedback from
the hardware, such as adaptively-spaced step scans.
Rehearse plans¶
Simply execute the plan as usual — RE(plan) — but define that plan
using the simulated motors and detectors from bluesky.examples instead of
the variables that represent real hardware.
RE(count([det])) # executes the plan, 'reading' the simulated detector
To avoid saving data from these “rehearsal” runs, make a separate instance of the RunEngine, and do not subscribe metadatastore.
SIM_RE = RunEngine({})
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.297 seconds)